Enhanced Heat Transfer |
||
Technology
Measurement Technology
Relevant Subjects
|
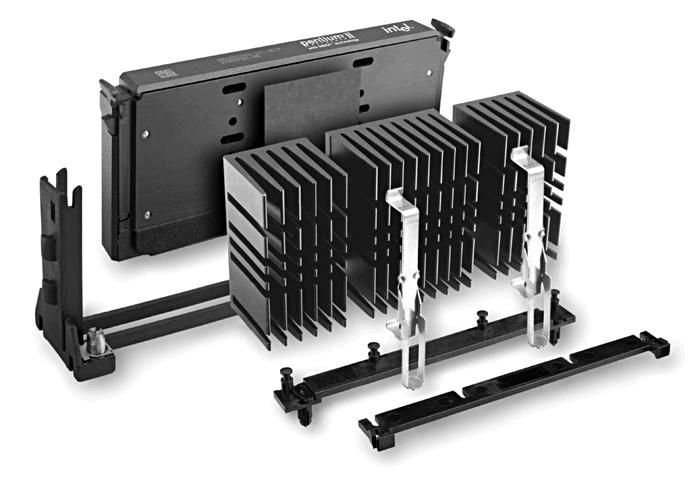
Cooling of Electronic Packages Electronic equipment has become increasingly important to our daily life. Improvement of these systems requires continued miniaturization of electronic components. However, one of the most significant restrictions to achieve this goal is the inability to dissipate enough heat from these very closely-spaced devices. Accordingly, poorly designed thermal management system will result in high operating temperatures for electronic equipment, leading to many potential problems or even premature failures. For example, in order to keep a Pentium CPU running smoothly, it is recommended by Intel that the maximum device junction (CPU die) temperature must not exceed 90 deg. C. Therefore, additional thermal enhancement to dissipate the heat is necessary. The most popular way of achieving that is to use a heat sink module as shown below.
Heat Sink Module for a Pentium II CPU Processor, from AAVID Thermal Products, Inc. It is nothing more than just a set of extended fin structures. By protruding out from the CPU chip using highly conductive materials, the heat sink module effectively increases the contact surface between the CPU unit and ambient air. According to Newton's cooling law, the amount of heat transfer through convection increases. When combining with a fan unit, the heat sink can significantly reduce the CPU temperature which allows the Pentium CPU to run smoother or even faster by overclocking at higher clock rates.
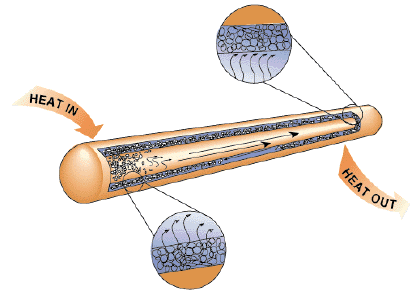
Heat Pipe Technology Unfortunately, the heat sinks usually are bulky and can not be used in systems where the space is limited, such as a laptop computer. Therefore, other heat transfer enhancing devices are necessary to reduce the temperature of a laptop CPU. One candidate to achieve this goal is the heat pipe technology. A heat pipe is a condenser-evaporator system in a simple form as a hollow tube with layers of wire screens along the wall to serve as a wick, as shown in the following figure.
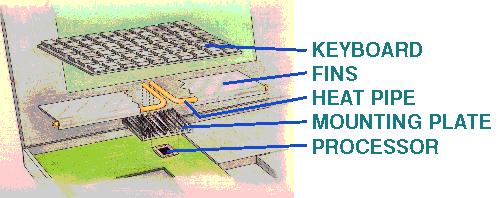
Schematic of a Heat Pipe Heat is transferred into the evaporator section to vaporize liquid. Vapor is returned to the condenser section and releases the heat to a heat sink by condensation at the other end. The liquid is returned to start the process over through a wick structure on the inside of the heat pipe. Heat pipe has an advantage that it has very low thermal resistance and its performance is relatively insensitive to its length. Consequently, it can be arranged in many shapes to accommodate different configurations. It has been successfully implemented in laptop computers. Shown below is a heat pipe connected to a laptop computer chip.
Heat Pipe Technology Used in a Laptop Computer
|
|